Benefits of Stem Cells
Stem cells offer numerous benefits in the field of regenerative medicine and healthcare. Some of the key advantages include:
Tissue Regeneration: Stem cells can repair damaged or degenerated tissues and organs, offering hope for conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Personalized Medicine: Induced pluripotent stem cells can be generated from a patient’s own cells, allowing for personalized treatment plans and reducing the risk of rejection in transplantation.
Reduced Ethical Concerns: The availability of non-embryonic stem cell sources, like iPSCs and adult stem cells, addresses ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cell research.
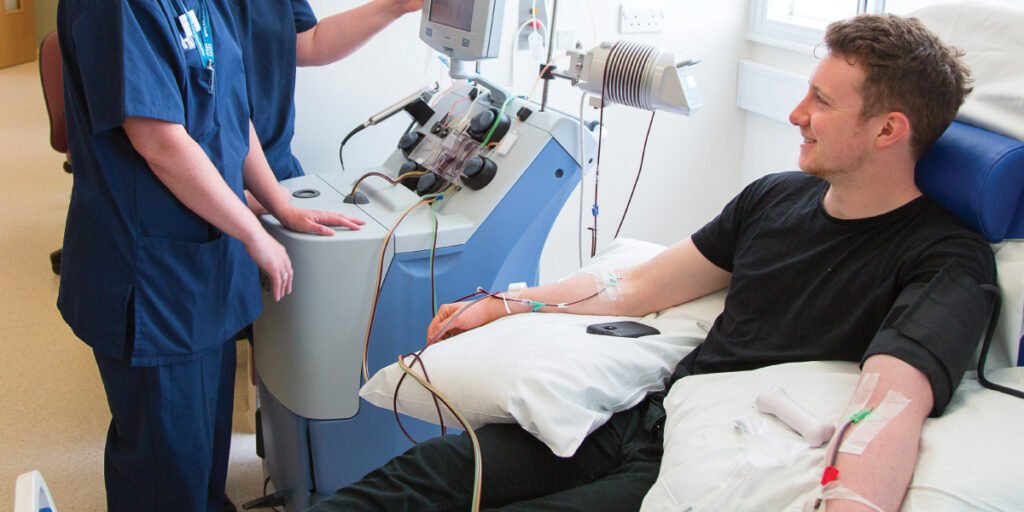
Treatment of Blood Disorders: Stem cells, particularly hematopoietic stem cells, are widely used for the treatment of blood-related conditions, including leukemia and lymphoma.
Immunomodulation: Mesenchymal stem cells have immunomodulatory properties, making them valuable in the treatment of autoimmune diseases and inflammatory conditions.
Research and Drug Development: Stem cells are instrumental in disease modeling and drug testing, enabling scientists to better understand diseases and develop new therapies.
Stem Cells in Healthcare, Learn more about Stem Cells visiting www.colombiastemcells.com